There has been an increase in the use of security technologies and, moreso, encryption. Indeed, encryption is a popular and increasingly essential element of the increasingly connected internet world.
Come to think of it, every time you browse through your favorite social media platform, log into your bank account, make a phone call to your friend, make a credit card transaction, or upload files to the cloud, you use encryption.


Encryption has played a great role in preventing the now surging cases of data breaches and stopping attackers from wreaking havoc with transportation infrastructure.
You might have heard someone use the term “encryption” and how it helps in data security. However, you still do not understand anything regarding the whole encryption concept. Worry not.
Your Guide To Understanding Basic Encryption Concepts:
In this article, we will explain to you in very simple terms everything you need to know about encryption, starting with what it is.
What is Encryption?
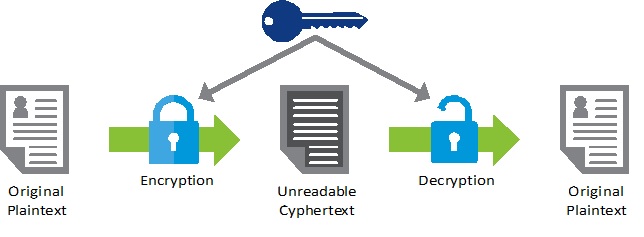
Encryption is a term used to refer to the method by which data and information are converted into a secret code that conceals the true meaning of the data. Encrypted data can only be read by the intended recipient, who bears the decryption key.
Essentially, encryption changes the message composition and format (not meaning) so that only people who know how to convert the message to its original format can read and decipher it.
An encrypted message will appear as a meaningless gibberish of characters and symbols. It won’t make any sense for someone to try and intercept an encrypted message because they won’t understand its meaning.
In computing terminologies, an unencrypted message is referred to as plaintext, whereas the encrypted data or message is called ciphertext. Ciphers are the formulas that are applied in encrypting and decrypting a message. We will, later on, learn more about how encryption works. For now, let us look at the history of encryption.
The History of Encryption
The term encryption derives its meaning from the Greek word Kryptos which means hidden, concealed, or secret. Encryption is not a modern-day invention, and in fact, its use can be traced back to the invention of the art of language.
As early as 1900 B.C, the Egyptians were already applying encryption algorithms in concealing inscription meanings. Although most people did not know how to read at the time, encryption models were soon developed to protect the secrecy of messages as they traveled from one point to another.
In 700 B.C., the Spartans applied encryption models to write sensitive messages on paper strips wrapped around sticks. The message became meaningless upon unwinding the tape. However, with the strip of a specific diameter, the receiver could recreate, read and decipher the message.
Perhaps one of the most famous applications of encryption was the Caesar shift cipher that was widely used by the Romans. This was a monoalphabetic cipher that shifted each letter of the alphabet by an agreed number. The reader was required to juxtapose the start of the alphabet until the entire message made sense.
There were other notable applications of encryption during the middle ages. It was not until the 1970s that encryption advanced, thanks to the publication of RSA and Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithms and the introduction of PCs.
How Does Encryption Work?
As we saw earlier, encryption takes plain text data such as email messages and scrambles them into an undecipherable format called ciphertext. Encryption, therefore, helps in safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of data, either stored on a computer device, cloud-storage system, or transmitted via a network such as an internet.
Upon the receiver receiving the message, he will use a secret decryption code to convert the encrypted message into a readable form. The process of converting ciphertext to plaintext is referred to as decryption.
To decrypt the message, both the sender and receiver of the message should have a secret key. An encryption key is a series of algorithms that will scramble and unscramble data through the encryption channel.
Symmetric And Asymmetric Encryption:
Symmetric encryption is one of the simplest but strong forms of encryption. It is essential for protecting data, whether the data is at rest, in transit, or stored in a cloud storage system. Symmetric encryption uses a single password or key to perform both encryption and decryption roles. This encryption form is sometimes referred to as secret-key encryption.

With symmetric encryption, once a file is encrypted, no third party will have access to it unless they have the secret key. The advantage of symmetric encryption is that it is fast and can be used in encrypting voluminous amounts of static data. The keys applied in symmetric encryption are usually 256 and 128-bits long.
There are several examples of Symmetric encryption systems. They include TripleDES, DES, AES-256, Advanced Encryption Standard, and Blowfish. Although Symmetric encryption systems have great advantages and encryption capabilities, their major limitation is their inability to share information across networks proficiently.
Another limitation is that Symmetric encryption keys often remain with the user and not the maker. It means that in case they get lost, it would be extremely hard for users to recover data.
Asymmetric Encryption, sometimes known as public-key encryption, applies a pair of mathematically-related keys in concealing data from prying eyes. It was developed majorly to solve the limitations of symmetric encryption of sharing data with multiple networks. The two mathematically-related keys used in Asymmetric Encryption are the public key and private key.
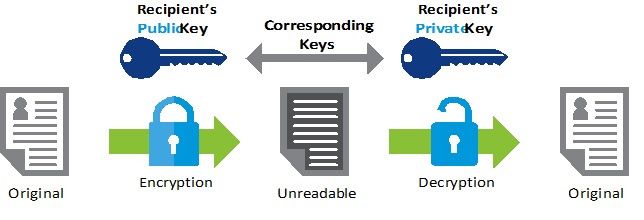

The key pair is created by mathematical formulas easy to solve on one side but very difficult to solve on the other side. It means that anyone can encrypt a message using the public key, which is freely made available by a service provider. However, only the holder of the private key can decrypt the message.
Asymmetric Encryption keys are usually 1024 or 2048 bits in length.
SSL Encryption
The SSL certificate is a perfect example that benefits from both symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption. It is the encryption that webmasters use to ensure safe communications between their website servers and clients’ browsers.
Amidst increasing cybersecurity threats and the rising costs of data breaches, the SSL certificate has established itself as the mainstay of website security. It allows for safe internet communications and transactions. All website users should leverage the power of encryption by purchasing and installing SSL certificates.
There has, however, been a question of SSL encryption on websites that have multi subdomains. You do not have to worry if your website has many subdomains. You just need to acquire a single wildcard SSL certificate, and you will be good to go.
You can look around for the best deal on wildcard lets say, a Cheap Essential SSL Wildcard will be a noteworthy option for securing domain and subdomains. You can still go with other brands also as per your like and requirement.
Why Does Encryption Matter?
There are three primary reasons why encryption is important. First and foremost, encryption plays a crucial role in protecting users’ online privacy. It achieves this role by converting plaintext data into ciphertext. It is important to ensure that all your email messages are encrypted and sent over an encrypted session.
Secondly, we all know that data insecurity threats have become a big concern in the internet world. Many of the large-scale data breaches that have occurred in the past have left millions of sensitive data exposed. Such data would not have been exposed would they had been encrypted.
Last but not least, data encryption is important for regulation compliance. For instance, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) require that healthcare providers implement security protocols that will help to safeguard users’ data and privacy. Encryption helps businesses to stay compliant with such regulations.
Conclusion
With the increasing cybersecurity threats, it is important that webmasters install adequate security measures to safeguard themselves and their users from data-related threats.
Encryption has for long been a great tactic that ensures utmost data security. However, despite its significance, most people still do not know what it is or how it operates. This article has explained some of the basic concepts of encryption that you need to know.